Introduction to Operating Systems
Introductory level operating system ideas, techniques, and implementations. This course is divided into four parts: (1) Virtualization, (2) Memory Management, (3) Concurrency, and (4) Persistence. Examples of practical applications include implementing a command line interpreter, and multi-threaded operating system tools.
Select From Ready-Made Modules to Build Your Course
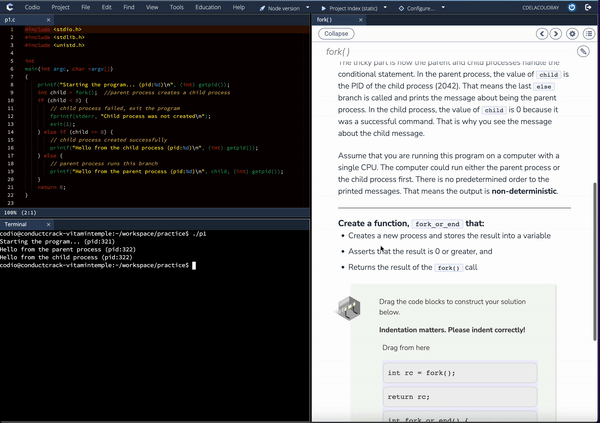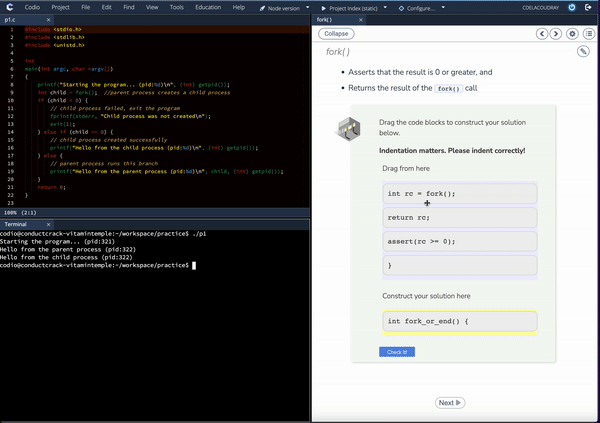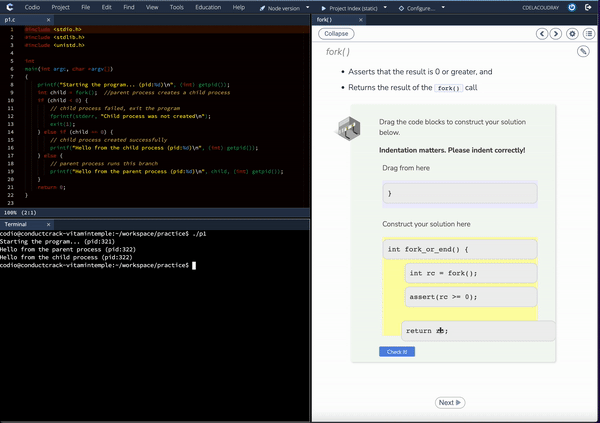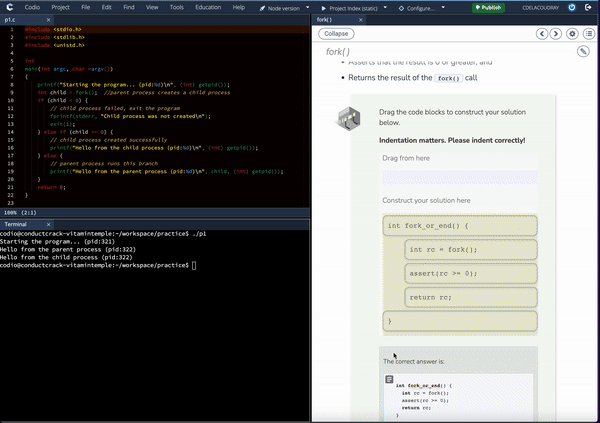
Deploy as-is, augment existing content, and effortlessly customize content and labs with our integrated AI Curriculum Assist tools.
Introduction to Operating Systems
Included in this course:
Building Expertise Through Hands-On Practice
Constructing Knowledge Through Coding
Introduction to Operating Systems emphasizes students applying and exploring the information presented. A code editor accompanies each page with new concepts so students can see for themselves how the computer responds to code. In addition, the content provides code snippets to get students started as well as suggested avenues for investigation.
Auto-graded assessments
Auto-Graded Assessments
Students receive immediate, rich feedback. In addition to correctness feedback (i.e. right or wrong), students will also see an explanation with the complete solution. There are a wide variety of questions — all of which are auto-graded, giving students a sense of their understanding of the material right after they are introduced to it and as they attempt harder and harder problems.
[Build] Real-World Coding Skills With Hands-On, Interactive Labs